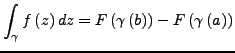Next: Cauchys Integralsatz v.2
Up: Cauchys Integralsatz
Previous: homotop, einfach zusammenhängend
Contents
Index
Cauchys Integralsatz
Sei
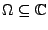 ein Gebiet, das einfach zusammenhängend
ist. Dann hat jede holomorphe Funktion
ein Gebiet, das einfach zusammenhängend
ist. Dann hat jede holomorphe Funktion
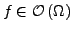 eine Stammfunktion auf
eine Stammfunktion auf 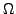 .
.
Insbesondere gilt für jeden s.s.d. Weg 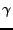 in
in 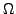 , dass
, dass
wobei
![$ \gamma:\left[a,b\right]\rightarrow\Omega$](img134.png) und
und 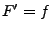 . Wenn
. Wenn
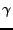 ein geschlossener Weg ist,
ein geschlossener Weg ist,
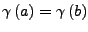 ,
so folgt also
,
so folgt also
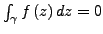 .
.
Marco Möller 20:58:46 15.11.2006
![]() ein Gebiet, das einfach zusammenhängend
ist. Dann hat jede holomorphe Funktion
ein Gebiet, das einfach zusammenhängend
ist. Dann hat jede holomorphe Funktion
![]() eine Stammfunktion auf
eine Stammfunktion auf ![]() .
.
![]() in
in ![]() , dass
, dass