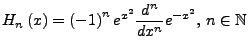Next: Integration
Up: Reelle Funktionen
Previous: Funktionenfolgen
Contents
Index
Subsections
Trigonometrische Funktionen
Sinus und Cosinus
Additionstheoreme
PI 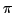
Die kleinste positive Nullstelle des Cosinus heißt per Definition
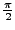 . Auf diese Weise definieren wir die Zahl
. Auf diese Weise definieren wir die Zahl
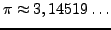
Hyperbolische Trigonometrische
Funktionen
Cosinus Hyperbolicus
Sinus Hyperbolicus
- Haben ihre Namen auf grund Ihrer Ähnlichkeit zu der Sinus und Cosinusreihe
- Tangens Hyperbolicus:
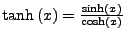
- Cotangens Hyperbolicus:
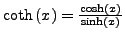
- Umkehrfunktionen: Arearfunktion existieren für alle Trigonometrischen
Funktionen, da diese alle streng monoton und stetig sind (zumindest
auf einem Teilintervall)
-
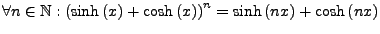
-
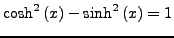
-
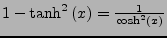
-
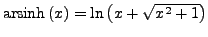
-

-
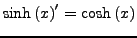
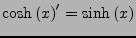
-
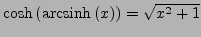
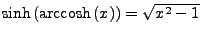
Hermite-Polynome
Die sogenannten Hermite-Polynome 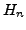 sind auf ganz
sind auf ganz
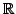 definiert durch
definiert durch
wobei
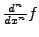 die
die 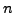 -te Ableitung von
-te Ableitung von 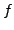 nach
nach
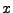 bezeichnet.
bezeichnet.
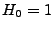
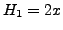
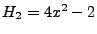
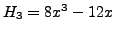
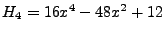
-
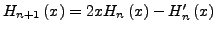
-
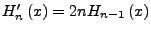
-
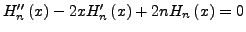
- Für
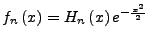 gilt
gilt
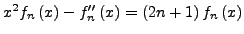
- Die
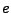 -Funktionen kürzen sich nach dem Ableiten herraus
-Funktionen kürzen sich nach dem Ableiten herraus





Next: Integration
Up: Reelle Funktionen
Previous: Funktionenfolgen
Contents
Index
Marco Möller 14:31:11 17.12.2005
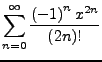
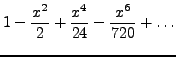
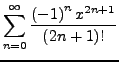
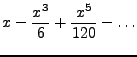
![]() . Auf diese Weise definieren wir die Zahl
. Auf diese Weise definieren wir die Zahl
![]()
![]() sind auf ganz
sind auf ganz
![]() definiert durch
definiert durch