




Next: Extremalprinzipien und thermodynamische Potentiale
Up: Extremalprinzipien, thermodynamische Potentiale
Previous: Prinzip der minimalen Energie
Contents
Index
Subsections
Legendre-Transformation thermodyn.
Potentiale
- Motivation
-
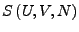 oder auch
oder auch
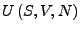 enthält alle Information über System. Gewünscht: Beziehungen, die
von den intensiven Variablen abhängen und dieselben Informationen
enthalten
enthält alle Information über System. Gewünscht: Beziehungen, die
von den intensiven Variablen abhängen und dieselben Informationen
enthalten
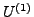 Übergang zu Funktionen die von Ableitungen
(z.B.
Übergang zu Funktionen die von Ableitungen
(z.B.
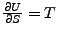 ) abhängen.
) abhängen.
- Allgemeine
- Beschreibung der Legendre-Transformation:
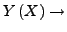 Suche Funktion die von
Suche Funktion die von
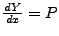 abhängt und die selbe Information
enthält.
abhängt und die selbe Information
enthält.
- Notwendige Vorraussetzung
- zu jedem
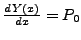 nur ein
nur ein 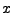 (invertierbar auf Definitionsbereich)
(invertierbar auf Definitionsbereich)
- entspricht:
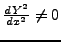 auf Definitionsbereich
auf Definitionsbereich
- eindimenstional
-
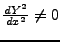
- Umkehrung
- durch nochmalige Anwendung der Legendre Transformation
- mehrdimensional
-
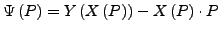
Helmholtz-Potential
- Transformation
-
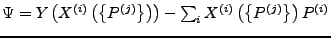
- Freie Energie
-
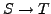
- Transformation
-
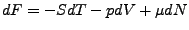
- Enthalpie
-
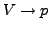
- Transformation
-
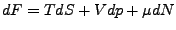
- Gibbs-Potential
-
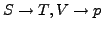
- Transformation
-
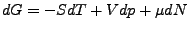
- Großkanonisches Potential
-
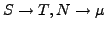





Next: Extremalprinzipien und thermodynamische Potentiale
Up: Extremalprinzipien, thermodynamische Potentiale
Previous: Prinzip der minimalen Energie
Contents
Index
Marco Möller 18:12:17 18.05.2006