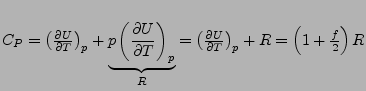Next: Zustandsänderungen
Up: Wärme
Previous: Wärmemenge und speziefische Wärme
Contents
Index
- Ideales Gas
-
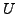 Innere Energie
Innere Energie
- Spezifische Wärmekapazität
-
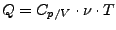
- konst. Volumen
-
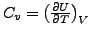
- konst. Druck
-
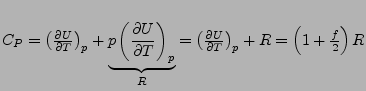
-
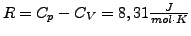
-
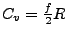
- Unterschied hängt mit der Arbeit zusammen, die ein ideales Gas leistet,
wenn es sich bei der Erwärmung ausdehnt.
- nur für Temperaturen ca. zwischen
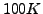 und
und 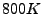
- für kleine Temperaturen Fällt
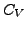 mit
mit 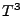 ab gegen 0.
Man sagt auch, die Freiheitsgerade frieren aus. Dies geschieht
um so später, je weniger freiheitsgerade vorhanden sind.
ab gegen 0.
Man sagt auch, die Freiheitsgerade frieren aus. Dies geschieht
um so später, je weniger freiheitsgerade vorhanden sind.
- Für große Temperaturen kommen zusätzliche Schwingungsfreiheitsgerade
hinzu, und
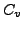 wird größer.
wird größer.
- Abiabatenexponent
-
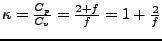
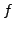 Freiheitsgerade des Gases
Freiheitsgerade des Gases
-
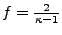
- Freiheitsgerade
-
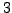 für
für 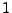 -Atomiges Gas
-Atomiges Gas
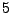 für
für 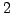 -Atomiges Gas
-Atomiges Gas
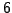 für
für 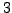 -Atomiges Gas
-Atomiges Gas





Next: Zustandsänderungen
Up: Wärme
Previous: Wärmemenge und speziefische Wärme
Contents
Index
Marco Möller 16:43:44 24.10.2005