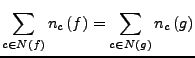Next: Berechnung trigonometrischer Integrale
Up: Residuen
Previous: Integration von meromorphen Funktionen
Contents
Index
Satz von Rouche
Sei
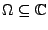 Gebiet,
Gebiet,
![$ \gamma:\left[a,b\right]\rightarrow\Omega$](img134.png) sei nullhomolog in
sei nullhomolog in 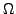 und einfach geschlossen. Weiter seien
und einfach geschlossen. Weiter seien
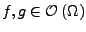 mit
mit
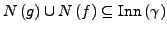 endlich.
endlich.
Falls gilt
für alle
![$ t\in\left[a,b\right]$](img496.png) so gilt
so gilt
- Summe der alg. Vielfachheiten ist gleich (die Funktionen haben gleichviele
Nullstellen).
Marco Möller 20:58:46 15.11.2006
![]() Gebiet,
Gebiet,
![]() sei nullhomolog in
sei nullhomolog in ![]() und einfach geschlossen. Weiter seien
und einfach geschlossen. Weiter seien
![]() mit
mit
![]() endlich.
endlich.